Characteristics of Almendra lake

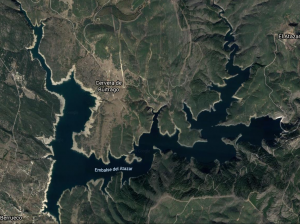
Practically as big as unknown, Almendra lake is the third largest in the country, only surpassed in capacity by the Alcántara and La Serena reservoirs. It has 2649 hm3 and a floodable area of 8650 hectares and is located on the Tormes River in the province of Salamanca.
Its main use is hydroelectric, although a good part of the municipalities in the west of Salamanca are supplied by its waters. Of course bathing and fishing in the summer months are activities that also take place in its waters. It is located in a very unpopulated environment in which human presence is practically imperceptible… Most of the villages that bathe its waters have barely a few hundred inhabitants.
Bottom composition and structures

If we talk about Almendra lake, we have to talk about the granite. Kilometres and kilometres of granite, with its typical more or less large “pebbles” and endless beaches of sand, coming from the degradation of these granites. In few reservoirs the granite is such a typical rock as in Almendra, where practically 100% of the bottom of the reservoir is formed by it.
Of course there are differences between the different areas, both in terms of slopes and in terms of size or state of degradation of the rocks. In general it is a reservoir with medium slopes, in which we can find really great depths, over 50 meters in the riverbed. However, there are also many areas with slight slopes where we can move tens of metres away from the bank without reaching much depth. There are also a number of large creeks on both the Zamora (northern) and Salamanca (southern) slopes.
The greatest handicap of this reservoir, from the point of view of predator fishing, is that the soil is very sandy and hardly contains any organic matter. This absence of organic matter means that the density of “prey” species is low and therefore the population of predators is also low.
Vegetation and cover

Normally it is a reservoir that is between 50 and 75% capacity, which makes the proliferation of vegetation in the streams that flow into it complicated. Some rainy years, in which the level remains high and stable during the spring months, there is a lot of underwater vegetation, especially in the main streams. However, in most years there is hardly any vegetation, except seasonally at these points and in small quantities.
On the other hand, there was a part of the floodable surface that was not cut down at the time, and we found areas with quite a few wood, mainly holm oaks. There are also some ash trees on creek bottoms when the reservoir is very low, but the holm oak is the dominant tree. In this case, the years in which the level is low are the best, as there is a greater percentage of trees submerged at a certain depth, and they come to the surface especially when the level drops. As it is a reservoir with little coverage of any kind, these areas of holm oaks are usually very important points to take into account.
Main fish species

The Almendra reservoir has never stood out for having high densities of predators. Due to its large size and what was said before about the bottoms, many times we will find kilometres and kilometres of shore not very productive… Even so, if we have the opportunity to frequent it we will end up finding fish.
Today the zander is the “queen” of the reservoir, although we can still find some pikes and black bass of good size.
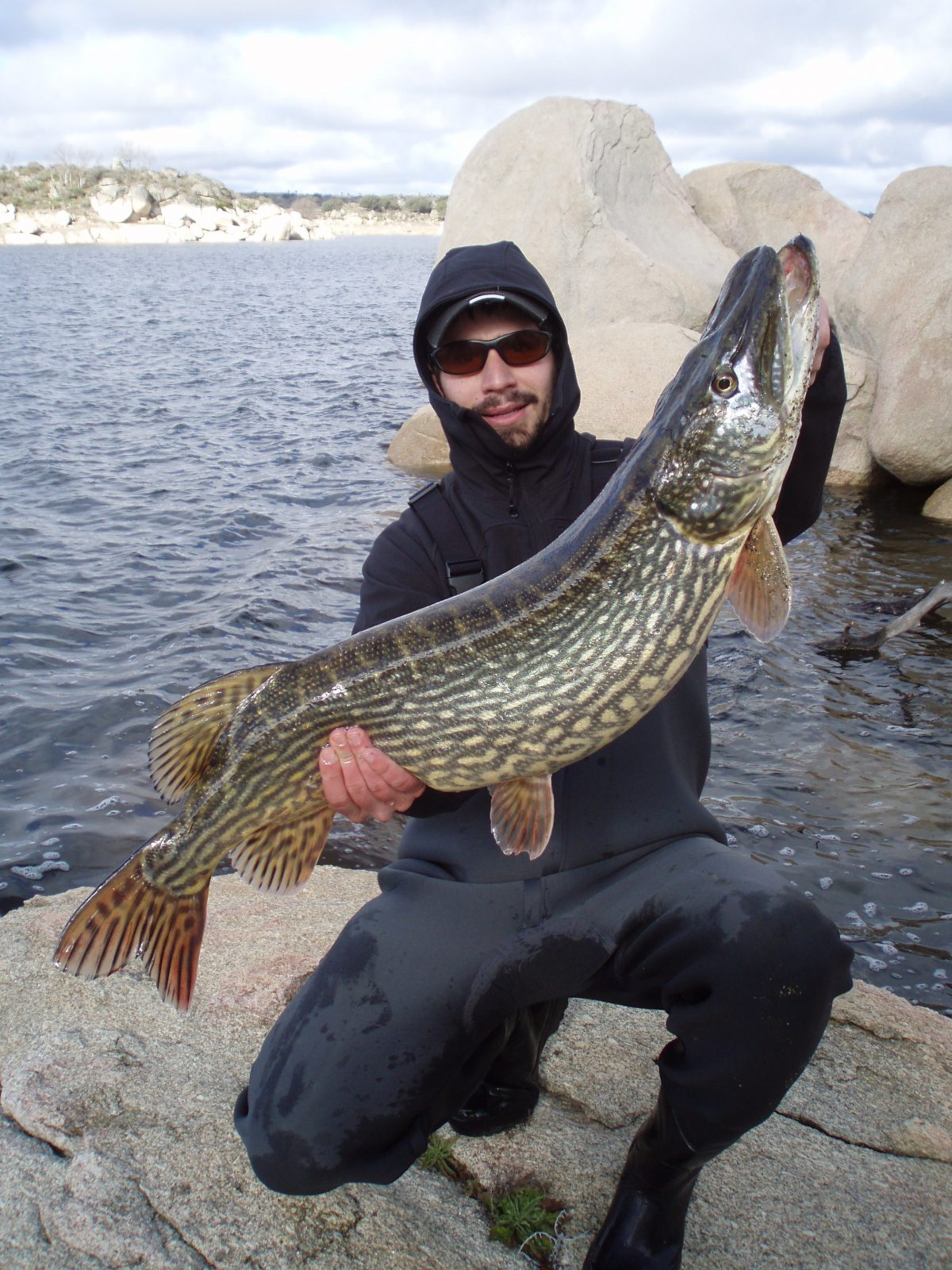
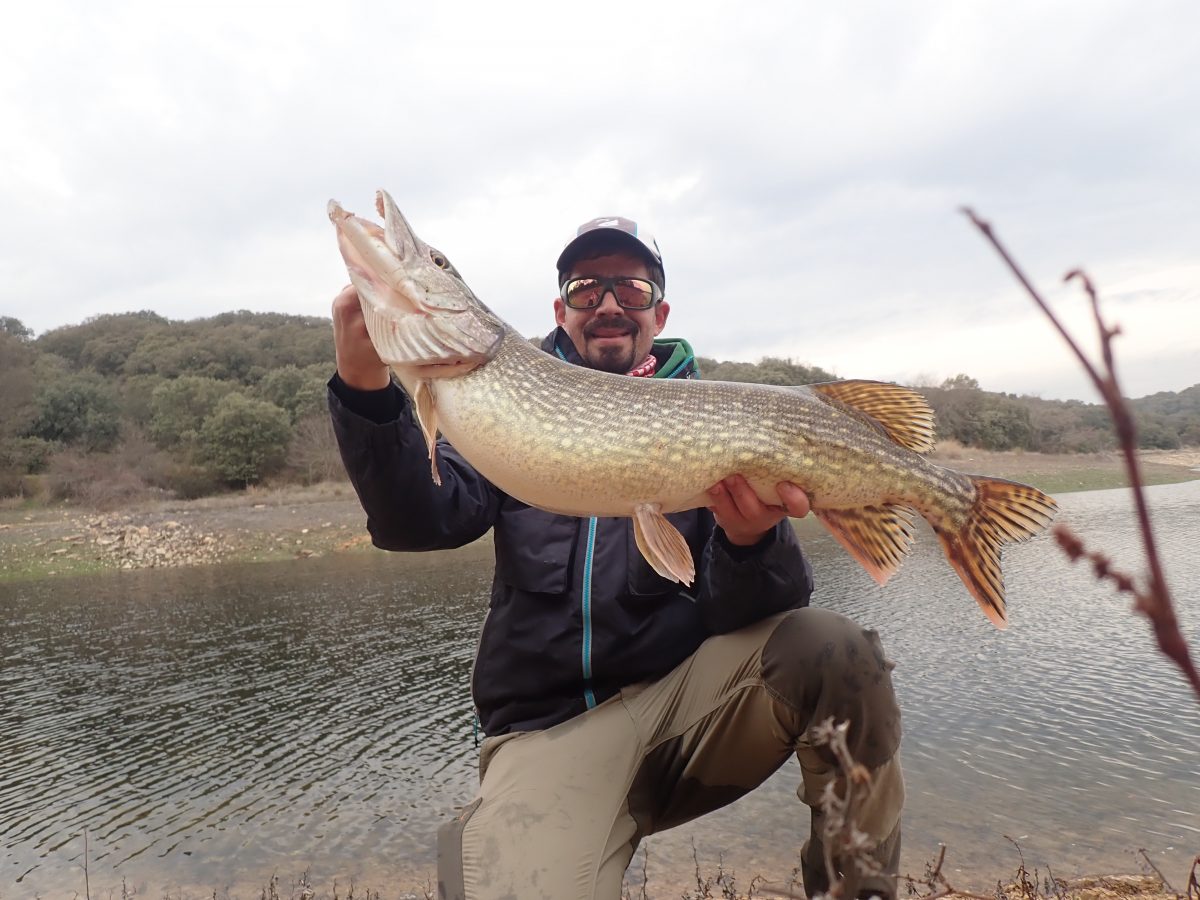
- Pike. In the past Almendra was famous for its great pikes. Practically every year, several specimens came out above two figures, some of them well above. Today it is very difficult to find them, although some still remain. Their main handicap is the lack of food, since the bleak has been scarce for several years.

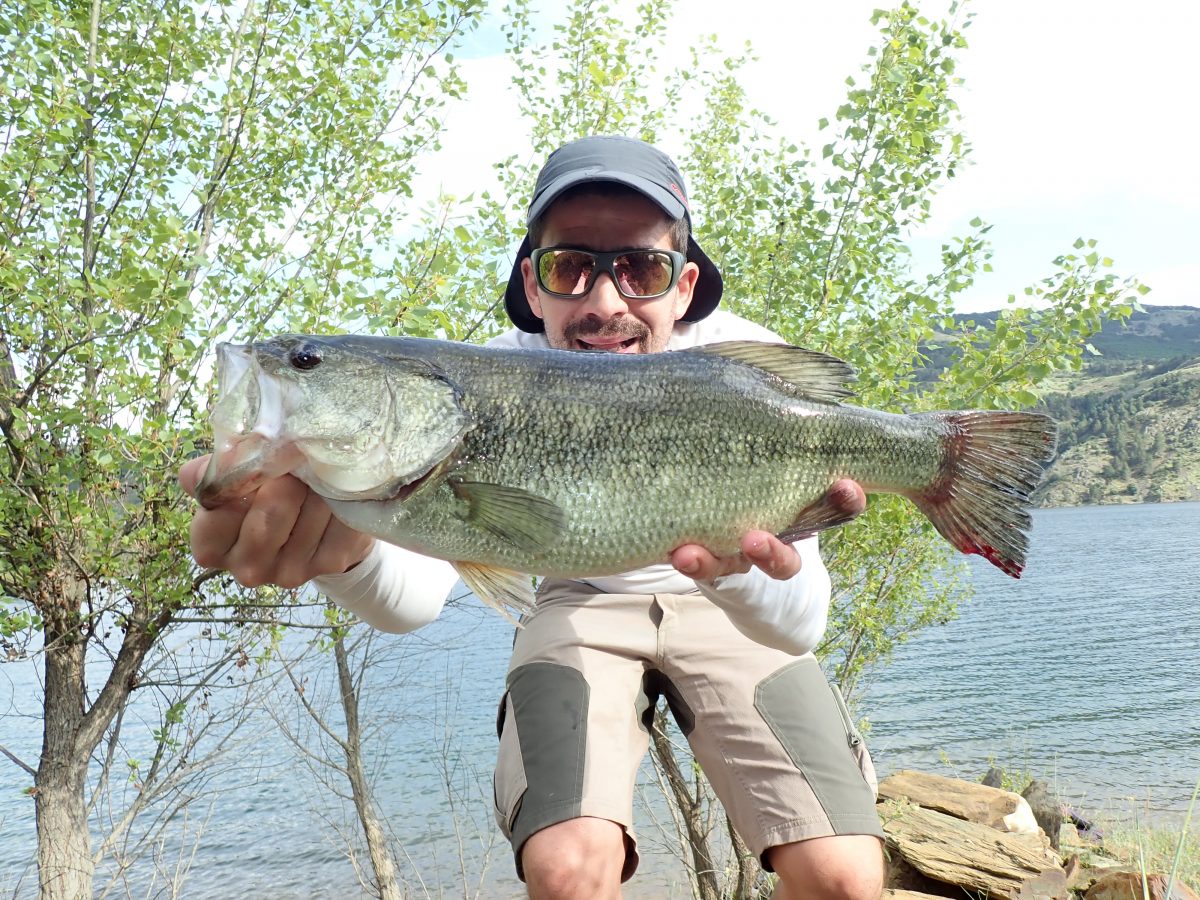
My PB in Almendra lake, over 2kg. - Black bass. Almendra lake has never stood out for its density of black bass nor for its size, but it has had times when pulling out a good handful of medium sized specimens was not complicated. The positive side is that it has a very low fishing pressure, and when you find them they usually bite quite well.
Another interesting species
- Zander. In recent years its population has grown exponentially, and is now stabilized or even slightly declining… It adapted really well to the reservoir and today we can catch very interesting specimens above 4 even 5 kg in weight. At certain times we can find interesting concentrations in which we can catch quite a few medium sized specimens. Its presence has had a very negative influence on the bleak population.

zander male in prespawn - Common barbel. The barbel in this reservoir has predatory behavior, especially in years when the level is low and there is not much food on the banks. In these cases, the small fish are part of their diet and become more aggressive towards the lures. The average size is very interesting (between 2 and 3 kg), and fish over 4 kg can be caught.
Prey species in Almendra lake

One of the main limiting factors in the development of predator populations in Almendra has always been the shortage of food. The bleak has been in the reservoir for tens of years, although its population never exploded. With the arrival of the zander, its population has been greatly reduced, and it is really difficult to find any bleak in the reservoir.
In addition to the bleak, the crawfish and the sunfish have always been present, although in rather low densities. And finally we would have the carp, crucian carp and barbel fry which, especially in spring, are a supplementary source of food.
Access and navigation
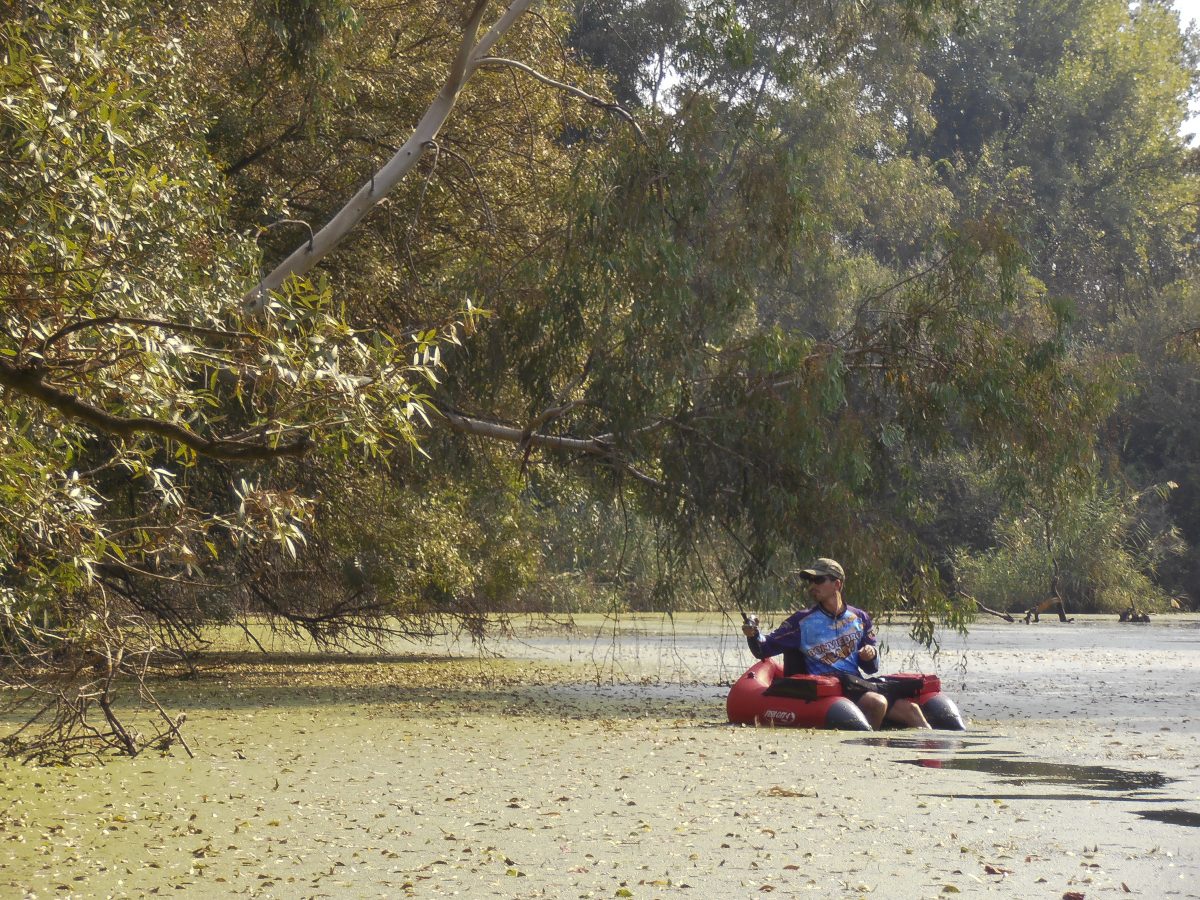
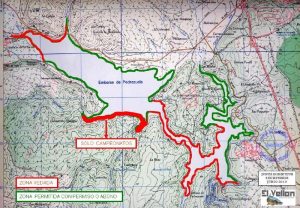
Almendra lake is navigable but you need to get a permit from the Duero River Basin, even to fish it from float tube or pontoon. As it is a reservoir with great changes of level and does not have a ramp, if we want to put our boat there we must know the accesses very well as it is not easy to find suitable areas.
It is a very extensive reservoir and although the banks are not excessively steep, there are not too many paths that end at the shore either, so we will have to walk a lot if we want to fish from the shore. Good luck to all the brave souls who dare to try their hand at this great lake.